A furniture designer is a person tasked to develop designs and specifications of furniture for manufacture. In this context, furniture design is considered to be part of the specialization of industrial design, however, interior designers may also do their work in order to make pieces that are custom to the interior spaces they are designing for. It is important to note that furniture designers not only focus on the aesthetic consideration of furniture pieces, but should also be particularly concerned with the aspect of furniture that relate to human usage and behavior, product appeal and fashion.
The Furniture Industry and its Opportunities
In designing furniture for manufacture, it is important to remember that designs to be made should be deliberate or intentional and should involve careful, organized and systematic logical thinking and planning. As a designer, the need to consider both functional and aesthetic aspects and pay particular attention to ergonomics, those factors that relate to ease of use and human behavior is essential. You will be tasked to prepare models and prototypes to demonstrate and test furniture for their functionality and durability. You will also be made to prepare effective drawings and illustrations to assist in the decision making process and support marketing efforts. In addition, the selection components and materials, resolution of assembly and manufacturing details and produce digital and documentary instructions for others involved in the manufacturing process will also part of your job. Lastly, the organization and overseeing of tooling to prepare for production and develop and oversee subsequent adjustments and refinements to the furniture.
Furniture design, though a specialization under product/industrial design, is also undertaken by interior designers and, traditionally, by architects. These designers may be seeking a unique style of furnishing for an interior or architectural project. Or they may be operating as a design consultant to a manufacturer, or as a manufacturing entrepreneur on their own behalf.
The Designer and its work
Purpose of Design
“FULFILLMENT OF HUMAN SATISFACTION”
Role of the Designer
Goals in Design
- Improvement of function or use of quality
- Improvement of production methods with the end view of reducing cost
- Improvement of distribution system with the end view of increasing sales
- Design innovation
FURNITURE DESIGN PROCESS
Basic Process of Development
There are 3 basic processes that help in the development of design.
- Understanding- this process involves programming, planning or simply the ideation stage of the design process. This is the baseline process that willl help the designer understand the different design problems that needed to be addressed. The design brief should be throughly understood so as to be able to provide an effective design solution.
- Synthesizing- this involves the inspirations and production stages of the the design process that involves combining the things obtained from the first stage and make a unified design. All researches, analysis and findings form the previous stage are collected to make a meaingful output.
- Evaluating- describes the process of testing and making objective judgment to the product produced from the first and second stages of the process. This is an opportunity for the designer to check the design for any flaws to be able to make the necessary iterations, and in order to make the appropriate improvements. This is like making the necessary final touches that would complete the design/product.

Creativity
This is a trait that every designer needs to have. Creativity is the process of coming up with new ideas. Creativity involves deliberate thinking that simply means “to make something, out of nothing”.
Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
- Intuitive Technique— is a technique that gives importance to quantity than quality, so the more ideas are produced, the better. Aha! moments basically comes abruptly and this techniques gives no restriction to these moments. Under this, the following methods may be performed:
- Brainstorming—involves the generation and processing of ideas by organized groups without limiting the imagination.
- Brain-writing— the output of brainstorming that is aimed to further develop the output listed.
- Alphabetical Listing— the process of listing down a number of solutions that corresponds to each letter of the alphabet. In this type of method, 26 solutions are made.
- Synectics— stimulates ideas and creativity by combining seemingly unrelated elements.
- Delphi Method— ideas and solutions are solved in a puzzle-like or riddle-like technique.
- Inversion— the opposite in this technique is being done by thinking of how to make a problem worse than solve it. This gives you the opportunity to see through things at a level that would prepare you for the worst-case scenario by increasing your awareness.
- Description be Association— lets you handle this by associating a problem with something else familiar.
- Logical or Systematic Technique—is based on the principle of splitting up the problem into sub problems and solving them one by one, using certain technique under these classifications.
- Morphology— redefines the problem first to an underlying more basic problem and then split up into its elements or sub-problems which can be varied independently from each other.
- Bionics— a technique that does not aim at stimulating the creative idea generating process, but systematically examines and analyzes objects of nature for possible adaptation as solution to some technical problems.
- Functional visualization— instead of thinking about what an object will look like, think about what function it will perform.
- Problem area analysis and Functional analysis— this logical approach will generally have a higher level of success. A comprehensive problem is split up into more and more minute sun-problems until the whole problem has become a network of interrelated problems.
Basic Criteria For Good Design
- The Physical and Physiological Factors- the provision for utilitarian requirement and bodily comfort is among the primary factor for a well-designed furniture. An effective design is that one that minimizes, if not eliminate bodily discomforts.
- The Historical and Cultural Factor- a good design does not neglect the historical and local cultural backgrounds. In order to design for the present, the past cultures would have been studied and considered.
- Aesthetic Consideration
- Structural Form Development- makes use of outlines and develops the forms of the furniture through these outlines. By connecting structural points, which are required either by construction or function, which are required either by consruction or function,variations on form are performed.
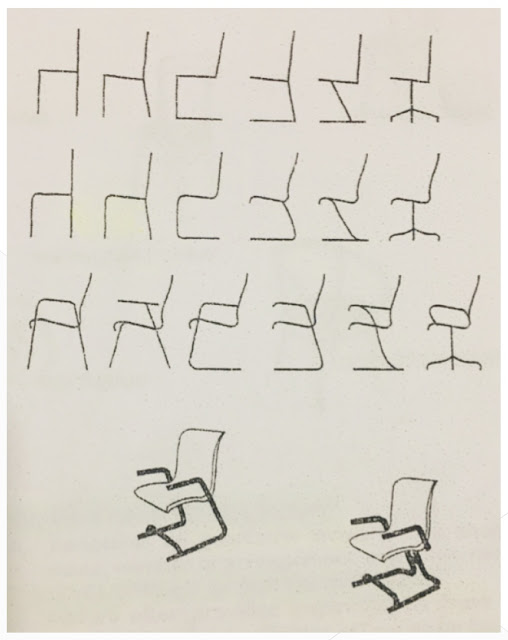
- Morphological Form Development- takes inspirations from existing designs and changes sevaral parts of that design that would produce improvements/ new design. Problem areas are looked into, and a continuos development of small changes applied to arrive at a more interesting term.
This type of design development describes, as seen in the illustration above that by changing the backrest design of an existing desig gives life to another design. And by further developing and changing the chair parts and elements, produced the “Bentwood Rocker” of Michael Thonet.
- Geometric Form Development- uses various geometric shapes, positions, angles, dimensions, sizes and arrangements as inspiration for designs.
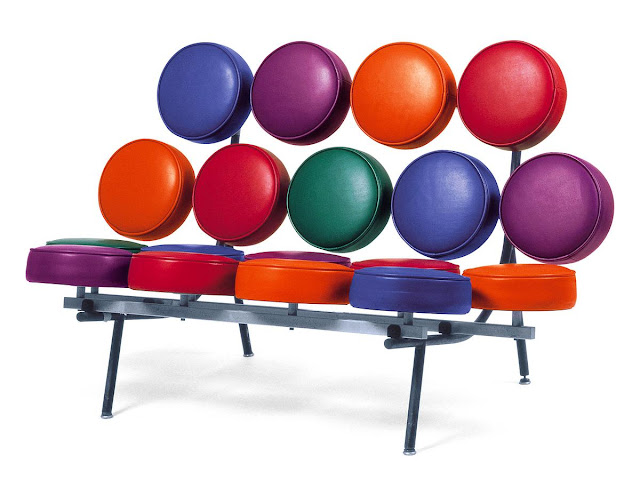
This type of design development as seen in the illustration as an example, uses the simple circular shape, and by employing the theory of design repetition, produced the renowned “Marshmallow Sofa” by the famous industrial designer, George Nelson.
- Form Development Based on Nature- anything seen with and about nature provides an abundant source of fresh ad exciting ideas, from the colors of the trees to shapes of the twigs of its branches. It offers immense possibilities of new ideas for design.
- Form Development Based from Various Sources- inspirations may be found other than nature, it can be from an event, food, a form of experience,emotion, religion, or just by anything that captivates the creative juices of the designer.





<3
ReplyDelete❤️
ReplyDelete